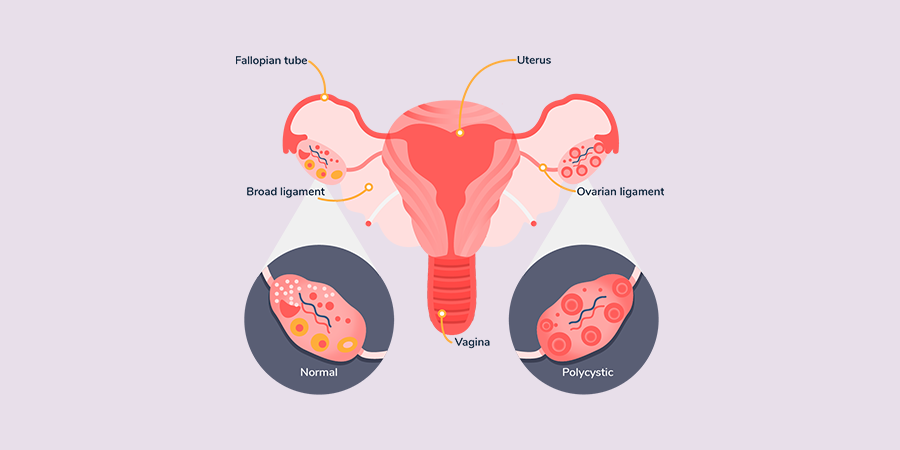
PCOS or Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is a common health condition that affects women of reproductive age all around the world. It is a hormonal imbalance that causes multiple problems in women. The hormones that cause this imbalance are estrogen, progesterone, and in particular androgen.
Typically, every month a follicle encloses an egg in the ovaries and releases it once it matures. The egg can then fertilize with a sperm, hence ending in conception or it can dissolve which results in menstruation.
With PCOS, the follicle does not release the egg instead the follicle stays enlarged and overtime becomes a fluid-filled cyst. This leads to the formation of many small cysts over the period.
Women with PCOS produce higher than normal amounts of male hormones, which causes hair growth on the face and body. It also causes us to skip our menstrual cycle and in some cases infertility.
Causes of PCOS:
The original cause of PCOS is still unknown but following are some known factors:
-
- Family history and genetics
- Hormonal imbalance
- Insulin resistance
- Increased androgen levels
- Weight
- Lifestyle
Symptoms of PCOS:
PCOS presents itself differently in individuals. Some women have mild symptoms while others have severe symptoms. Symptoms can also change over the years.
These symptoms may include:
-
Periods and fertility
- No periods or irregular, infrequent or heavy periods
- No ovulation
- Multiple cysts
- Difficulty becoming pregnant
- Miscarriages
- Health issues during pregnancy
- Infertility
-
Changes in body
- Excess facial and body hair
- Baldness
- Darkened skin patches
- Weight gain
- Pelvic pain
- Pain during sexual intercourse
-
Health issues
- Mood disorders
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Low self-esteem
- Earlier onset of diabetes
- Endometrial carcinoma
- Sleep apnea
Diagnosis of PCOS:
PCOS can be difficult to identify because of its complex and numerous symptoms. Doctors rule out other possibilities first before giving this diagnosis.
A diagnosis is made on a set criterion of 3 things:
- Irregular or no periods
- High androgen levels
- Cysts found in pelvic ultrasound
To confirm said diagnosis doctor will:
- Ask your Medical and family history
- Conduct a physical exam
- Order blood tests to check androgen level
- Do a pelvic ultrasound
- Do a hormone level test of FH, LSH, Estrogen, progesterone, TSH, and prolactin
Get yourself checked if you have irregular or no period for 2 months or more. Or if any of the other symptoms persist.
Management Goals for PCOS
Once you are diagnosed with PCOS, you need to take very good care of your health. Consult with your doctor and take measures to cure yourself.
To manage your PCOS you need to have:
- A good understanding of PCOS
- A healthy approach to lifestyle
- Appropriate medical therapies
- A complete focus on your body and mind

-
Weight Change
If you are overweight, losing even 5-10% of your body weight will affect your PCOS. Losing weight will improve:
-
- periods
- fertility
- mental health
- insulin levels
- testosterone levels
- risk of Type 2 diabetes and heart diseases
-
Pursue physical activity
Physical activity can have many health and mental benefits. It has shown to improve symptoms and its other benefits include:
-
- Reduced anxiety and depression
- Less stress
- Improved menstruation and fertility
- Weight maintenance
- Less difficulty in becoming pregnant
- Increased stamina and motivation
-
Dietary Changes
Be sure to make changes in your diet as well. Your diet affects 80% of your weight. So, make sure to include lean foods and limit processed foods. try to include fresh produce and as many healthy items as possible.
Treatment of PCOS
There’s no 100% cure for PCOS. Research has been done over the years and many medicines are undergoing trials. Time will tell whether medication for PCOS will be available or not.
Along with management goals for PCOS, it can be treated through the following medical treatments:
- Birth Control
Birth control contains estrogen and progesterone. Taking them daily can restore a normal hormone balance. It will also result in the regulation of ovulation. Excess hair growth will be controlled and it can also protect you against endometrial cancer. You can take birth control in the form of a pill, patch, shot, or vaginal ring.
- Metformin
Metformin is a drug used to treat type 2 diabetes. It can also treat PCOS by regulating insulin levels. It works alongside diet and exercise in managing weight. As a result, the menstrual cycle is improved and weight loss occurs.
- Clomiphene
Clomiphene is taken during the first part of the menstrual cycle. It is a fertility drug that can help women with PCOS to get pregnant.
- Letrozole
Letrozole improves fertility in women with PCOS and it is an ovulation-inducing tablet. It is used to stimulate the growth and release of an egg from the ovary.
- Gonadotrophins
FSH, LH, and hCG are hormones involved in ovulation. They are also used for treating infertility. They are injected in the body and the ovary is monitored by ultrasound to avoid overstimulation.
- Surgery
In rare cases, surgery can be done as well to improve fertility and to treat PCOS, if the body is unresponsive to other treatment methods.
When to see your doctor?
See your doctor if you have:
- Irregular periods for more than 3 months
- You have no periods and are not pregnant
- Excess facial or body hair growth
- Experience pain during sexual intercourse
- Unexplained weight loss
- Been trying to get pregnant for more than a year but are not successful
























